The UnEssay: ANTHR-140 Final
An alternative assessment that tests knowledge through a method other than the typical essay.
What is evolution, and how does it occur?
Have you ever wondered how animals share a common ancestor, yet somehow manage to be so different from one another? The answer lies in evolution, a process in which various species develop various features because of their environment. However, these developments happen in various methods, often known as the four forces of evolution. They are: genetic drift, gene flow, natural selection, and mutation.
This website will guide you toward explaining these four forces of evolution in a simple manner, skipping the specific terminology and giving you a general overview, provided with visuals to solidify your understanding.
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift is a random change in allele frequencies during meiosis. More specifically, the allele has two choices: be lost or fixed. It is most noticeable observing at the macro scale, since each generation has different frequencies being passed on.
Genetic drift can occur in two different ways: the founder effect and genetic bottleneck.
Founder effect
The founder effect happens when a population spreads to a new area, but since it’s a smaller sample, it has less genetic diversity compared to the original range of the previous population. A good way to remember the founder effect is that the population that migrates are the “founders” of that community within that geographic region.
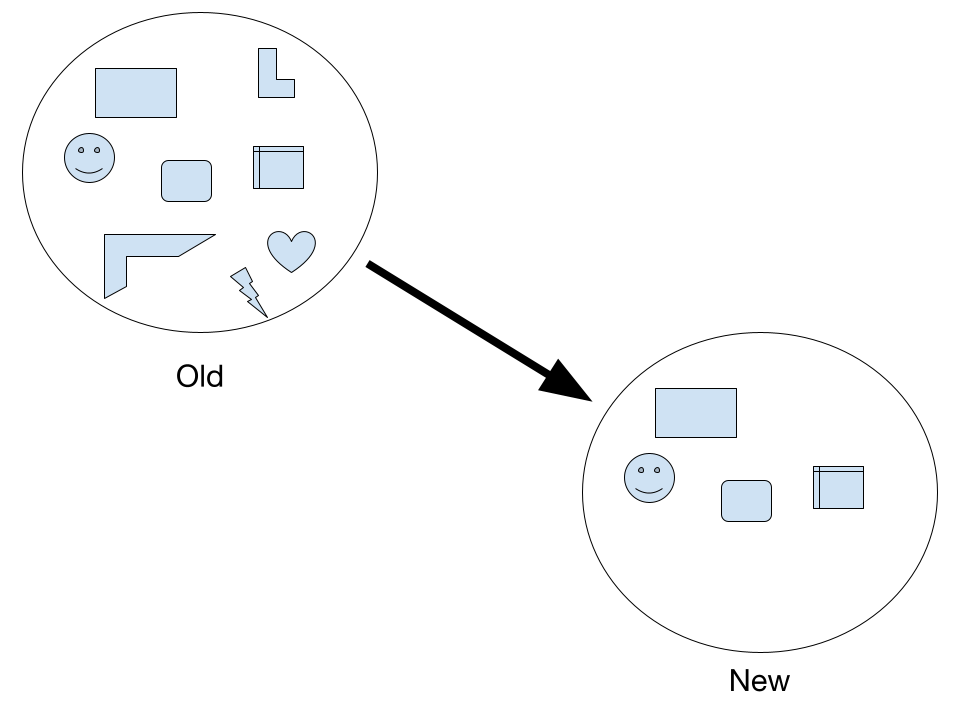
A real life situation of this would be royal inbreeding. In an attempt to keep the bloodline pure, royalty often had problems mating with their own family. Hemophilia was particularly prevalent within the British Royal Family. While these symptoms would have a small chance to appear in large populations, because the sample size is so small, the change of receiving the specific trait is amplified.
Genetic bottleneck
Unlike the founder effect, genetic bottleneck happens when a major reduction in population occurs, and its survivors can only reproduce a less diverse generation because the survivors do not have as wide of a variety in traits as the original population.
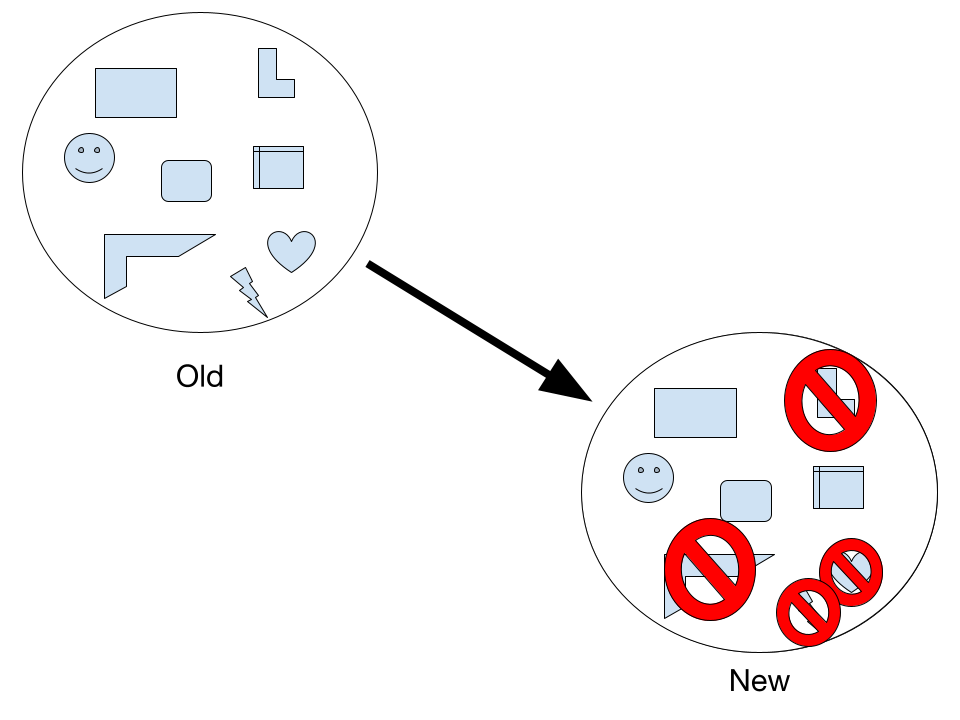
A real life example of this would be all the animals throughout the various mass extinctions.
Gene Flow
When two species have different allele frequencies get together, and mix the allele variants within each other, gene flow occurs. Gene flow is the movement of alleles from one population to another or a simpler way to put it, migration.
One thing to note is that while the new generation becomes more similar over time compared to its predecessors, the amount of variety within that generation also increases.
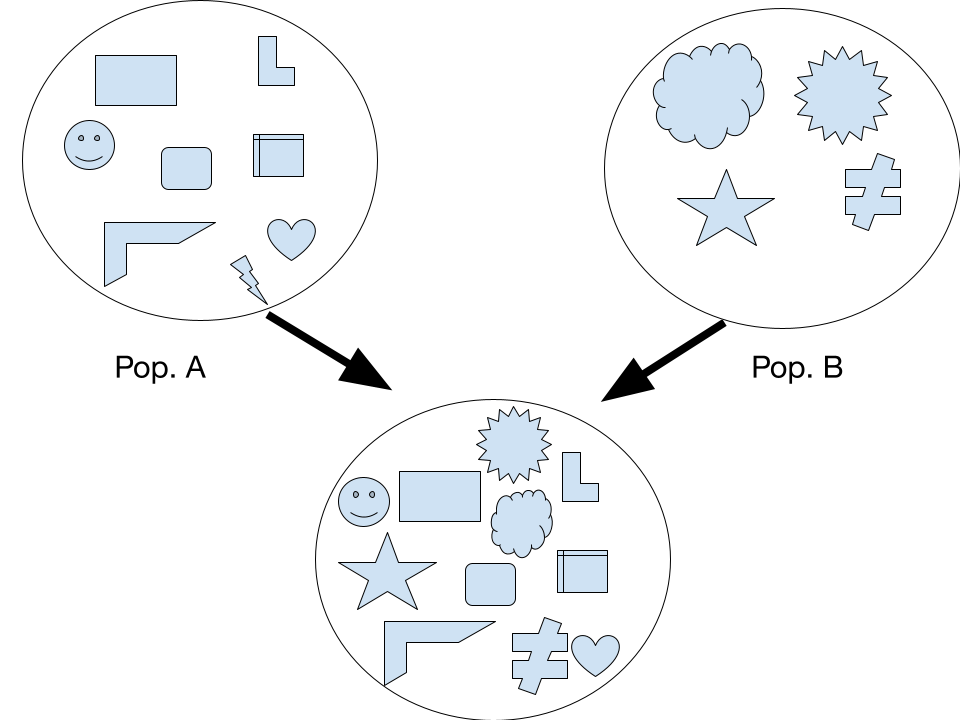
Gene flow actually occurs in our daily lives. Since gene flow’s greatest factor is geographical distance, the advent of global interconnectivity has allowed for humans to mingle across various geographical regions.
Natural Selection
Natural selection specifically acts upon variation, where those best adapted to their environment will live the longest and reproduce. The extent to which they are able to survive is measured as fitness. It is important to note that natural selection cannot produce new traits, and only picks what is already in the environment.
There are three types of natural selection: directional, disruptive, and stabilizing.
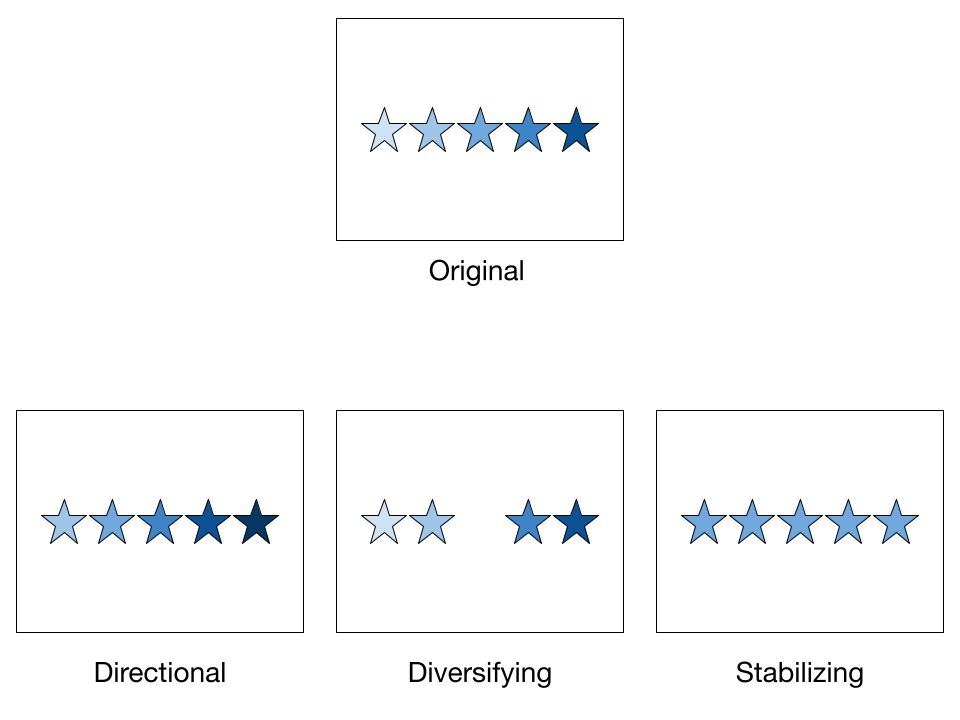

- directional
- heavily prefers one side
- ex: giraffes with longer necks get access to more food
- diversifying (or disruptive)
- splits out toward the two extremes
- ex: more white moths lived because its environment was mostly white, then more black moths lived because of the Industrial Revolution
- stabilizing
- skews toward the mean of two traits
- ex: babies cannot be too heavy or too light, they have to just right
Natural selection doesn’t have to be beneficial in just living, but also reproducing as well. This is called sexual selection, where certain traits can allow for species with certain traits to be more prevalent because of the trait’s attractiveness.
What’s the difference between genetic bottleneck and natural selection?
One question that came up when I was researching for this was the difference between the two. While both involve a loss of population, genetic bottleneck has a loss of diversity because the species was killed at random, while natural selection leaves those with specific traits alive.
Mutation
Mutation occurs when a random mistake in the DNA’s amino acids is made, and is the only force of evolution that develops new alleles. Mutations can have positive, negative, or neutral effects.
While most mutations have no effect, an example of a positive mutation occurs with the people who lived through the Black Death. Because they were resistant to the disease, their descendants not only have a resistance to the Black Death, but related morbidities such as HIV.
Mutation can occur in various ways, and I’ll go over two briefly:
Point mutation
Accidentally substituted one amino acid for another, which produces an entirely different protein.

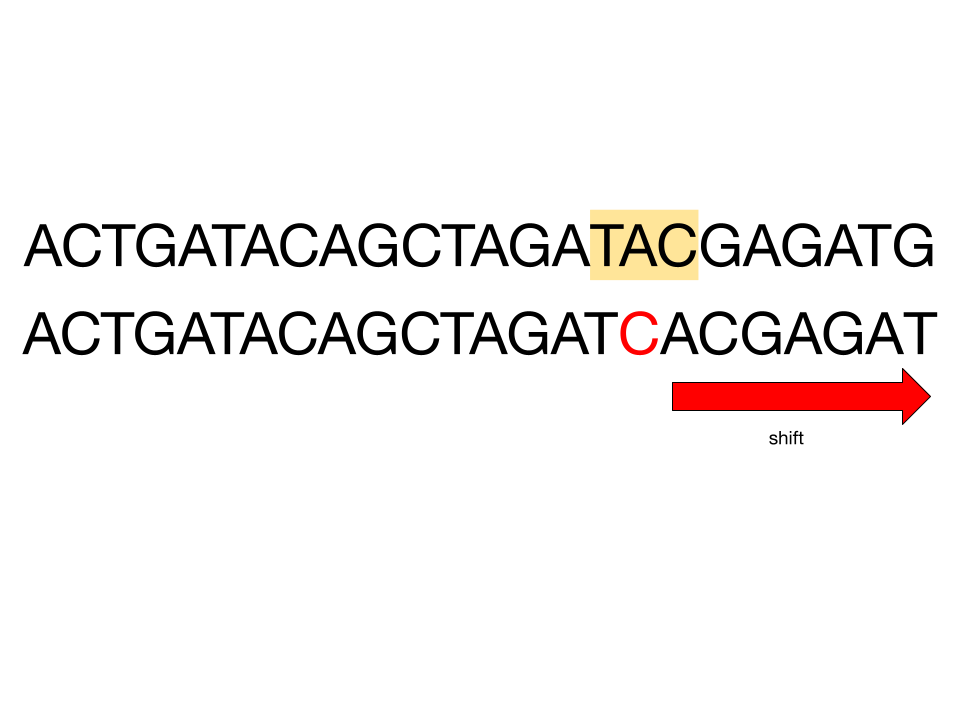
Frameshift mutation
Unlike point mutation, frameshift mutation instead adds a letter, which is more detrimental because it shifts other letters. This means that instead of producing an entirely different protein once, it affects the rest as well.
Some other types of mutation include transposable elements, chromosomal mutation, spontaneous mutation, and induced mutation.